If you're new to Kubernetes, getting started can feel overwhelming. A solid introduction to Kubernetes goes beyond basic concepts—it requires hands-on practice, a deep understanding of the Kubernetes framework, and knowledge of real-world applications. In this guide, we’ll explore collaborative learning methods, advanced topics, and real-world cases to help you handle Kubernetes with confidence.
Kubernetesis an open-source container orchestration system used for automating computer application deployment, scaling, and management. In other words, you use Kubernetes to make serious magic with containers. It has a large, rapidly growing ecosystem. Kubernetes services, support, and tools are widely available.
The name Kubernetes originates from Greek, meaning helmsman or pilot. Google open-sourced the Kubernetes project in 2014. Kubernetes combinesover 15 years of Google's experiencerunning production workloads at scale with best-of-breed ideas and practices from the community.
Here’s how Dan Kohn, executive director of theCloud Native Computing Foundation(CNCF),in a podcast with Gordon Haff, explained it: “Containerization is this trend that’s taking over the world to allow people to run all kinds of different applications in a variety of different environments. When they do that, they need an orchestration solution to keep track of all of those containers and schedule them and orchestrate them. Kubernetes is an increasingly popular way to do that.”
Containers are a good way to bundle and run your applications. In a production environment, you need to manage the containers that run the applications and ensure that there is no downtime. For example, if a container goes down, another container needs to start. Wouldn't it be easier if this behavior was handled by a system?
That's how Kubernetes comes to the rescue! Kubernetes provides you with a framework to run distributed systems resiliently. It takes care of scaling and failover for your application, provides deployment patterns, and more. For example, Kubernetes can easily manage a canary deployment for your system.
Kubernetes provides you with:
When you deploy Kubernetes, you get a cluster.
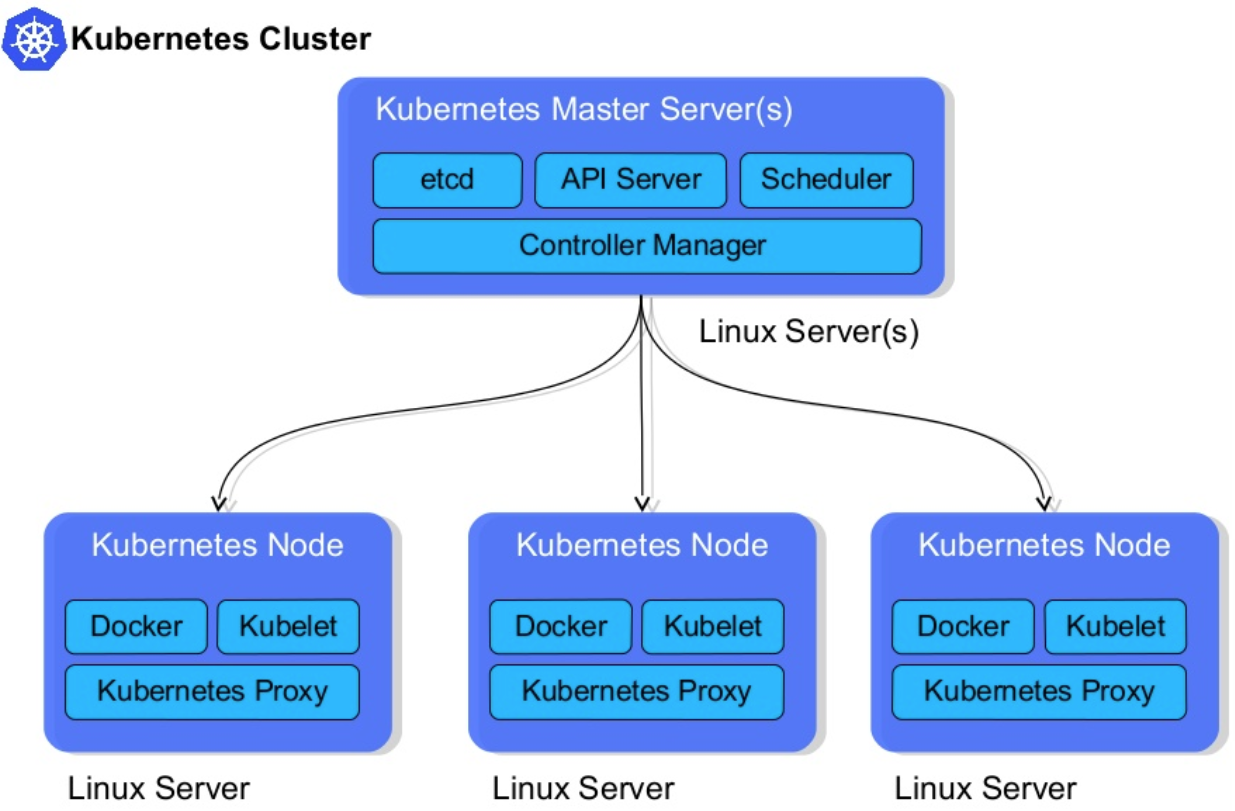
A Kubernetes cluster consists of a set of worker machines, callednodes, that run containerized applications. Every cluster has at least one worker node.
The worker node(s) host thePodsthat are the components of the application workload. Thecontrol planemanages the worker nodes and the Pods in the cluster. In production environments, the control plane usually runs across multiple computers and a cluster usually runs multiple nodes, providing fault-tolerance and high availability.
Control Plane Components
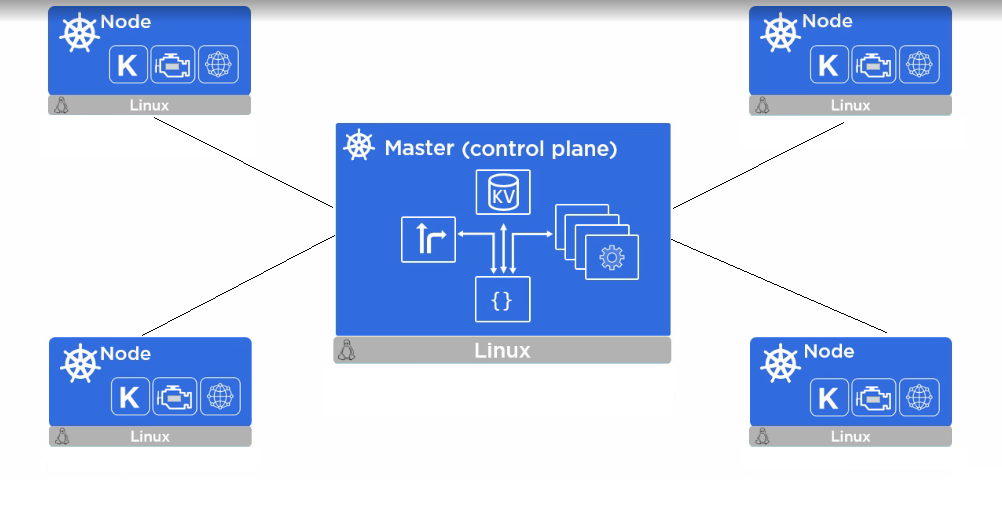
The control plane's components make global decisions about the cluster (for example, scheduling), as well as detecting and responding to cluster events (for example, starting up a newpodwhen a deployment's replicas field is unsatisfied).
Control plane components can be run on any machine in the cluster. However, for simplicity, set up scripts typically start all control plane components on the same machine, and do not run user containers on this machine.
The API server is a component of the Kubernetescontrol planethat exposes the Kubernetes API. The API server is the front end for the Kubernetes control plane.
The main implementation of a Kubernetes API server iskube-apiserver. kube-apiserver is designed to scale horizontally—that is, it scales by deploying more instances. You can run several instances of kube-apiserver and balance traffic between those instances.
Consistent and highly-available key-value store used as Kubernetes' backing store for all cluster data.
If your Kubernetes cluster uses etcd as its backing store, make sure you have abackupplan for those data.
Control plane component that watches for newly createdPodswith no assignednode, and selects a node for them to run on.
Factors taken into account for scheduling decisions include individual and collective resource requirements, hardware/software/policy constraints, affinity and anti-affinity specifications, data locality, inter-workload interference, and deadlines.
Control Plane component that runscontrollerprocesses.
Logically, eachcontrolleris a separate process, but to reduce complexity, they are all compiled into a single binary and run in a single process.
These controllers include:
A Kubernetescontrol planecomponent that embeds cloud-specific control logic. The cloud controller manager lets you link your cluster into your cloud provider's API, and separates the components that interact with that cloud platform from components that just interact with your cluster.
The cloud-controller-manager only runs controllers that are specific to your cloud provider. If you are running Kubernetes on your premises, or in a learning environment inside your PC, the cluster does not have a cloud controller manager.
As with the kube-controller-manager, the cloud-controller-manager combines several logically independent control loops into a single binary that you run as a single process. You can scale horizontally (run more than one copy) to improve performance or to help tolerate failures.
The following controllers can have cloud provider dependencies:
Node components run on every node, maintaining running pods and providing the Kubernetes runtime environment.
An agent that runs on eachnodein the cluster. It makes sure thatcontainersare running in aPod.
The kubelet takes a set of PodSpecs that are provided through various mechanisms and ensures that the containers described in those PodSpecs are running and healthy. The kubelet doesn't manage containers that were not created by Kubernetes.
kube-proxy is a network proxy that runs on eachnodein your cluster, implementing part of the KubernetesServiceconcept.
kube-proxymaintains network rules on nodes. These network rules allow network communication to your Pods from network sessions inside or outside of your cluster.
kube-proxy uses the operating system packet filtering layer if there is one and it's available. Otherwise, kube-proxy forwards the traffic itself.
The container runtime is the software that is responsible for running containers.
Kubernetes supports several container runtimes:Docker,containerd,CRI-O, and any implementation of theKubernetes CRI (Container Runtime Interface).
Addons use Kubernetes resources (DaemonSet,Deployment, etc) to implement cluster features. Because these are providing cluster-level features, namespaced resources for addons belong within the kube-system namespace.
Selected addons are described below.
While the other addons are not strictly required, all Kubernetes clusters should havecluster DNS, as many examples rely on it.
Cluster DNS is a DNS server, in addition to the other DNS server(s) in your environment, which serves DNS records for Kubernetes services.
Containers started by Kubernetes automatically include this DNS server in their DNS searches.
The dashboardis a general-purpose, web-based UI for Kubernetes clusters. It allows users to manage and troubleshoot applications running in the cluster, as well as the cluster itself.
Container Resource Monitoringrecords generic time-series metrics about containers in a central database and provides a UI for browsing that data.
Acluster-level loggingmechanism is responsible for saving container logs to a central log store with a search/browsing interface.
A strong foundation in the Kubernetes framework is important for effective cluster management. Kubernetes operates using a Kubernetes API, which serves as the central point of communication between users, cluster components, and external tools.
The core components include:
By mastering these elements, you can optimize cluster performance and troubleshoot issues effectively.
The theory about Kubernetes is okay. However, without experience, you are the same as a beginner. Platforms like Minikube, Kind, and Play with Kubernetes provide environments where you can test Kubernetes controls without setting up a full system. These tools help you investigate Kubernetes cluster setups, workload scaling, and troubleshooting.
For example, practicing Kubernetes deployment by launching containerized applications and automating rollouts ensures you’re prepared for production scenarios. Collaborative labs provide step-by-step exercises to strengthen learning, making it easier to apply Kubernetes in real-world settings.
Once you've understood the basics, it's time to explore more complex topics:
Securing an AWS Root Account is an important best practice for professionals managing cloud security. Understanding these latest topics will also make you ready for large organization-level Kubernetes implementations and certifications like the AWS Certified Solutions Architect exam.
Organizations worldwide use Kubernetes to streamline operations. Some key examples include:
By understanding these practical applications, you can make informed decisions when executing Kubernetes in your projects.
Kubernetes (k8’s) is the next big wave in cloud computing, and it’s easy to see why as businesses migrate their infrastructure and architecture to reflect a cloud-native, data-driven era.A strong introduction to Kubernetes needs more than just theoretical knowledge—you need hands-on experience, architectural insights, and exposure to advanced concepts. Whether you're an aspiring cloud professional or an experienced DevOps engineer, mastering Kubernetes will open doors to high-paying roles. Ready to take the next step? Explore expert-led Kubernetes training at NovelVista and elevate your cloud career today!
Master the art of container orchestration with the Certified Kubernetes Administrator (CKA) course.
👉 Enroll Now in CKA Certification Training