To be honest, cloud networking can feel like too much to handle at times. Subnets, route tables, VPC scanning, security groups… It’s a lot to learn! But here’s the thing: You must know about Amazon Virtual Private Could (VPC) if you're working with AWS.
Amazon Virtual Private Cloud guarantees safety, scalability, and speed in case you are building a multi-tier cloud solution or a simple web app. But how do you get it right? Let's break it done into simple steps.

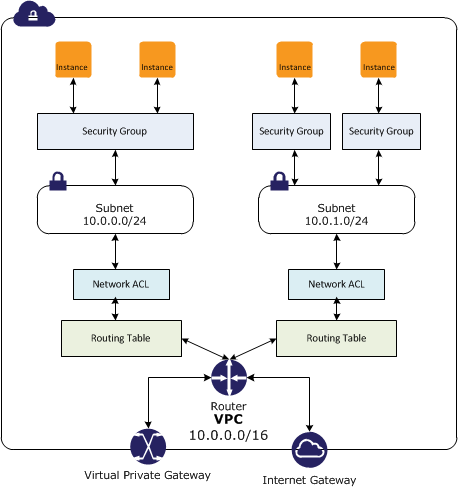
Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (Amazon VPC) is a service that lets you launch AWS resources in a logically isolated virtual network that you define. You have complete control over your virtual networking environment, including selection of your own IP address range, creation of subnets, and configuration of route tables and network gateways. You can use both IPv4 and IPv6 for most resources in your virtual private cloud, helping to ensure secure and easy access to resources and applications.
As one of AWS's foundational services, Amazon VPC makes it easy to customize your VPC's network configuration. You can create a public-facing subnet for your web servers that have access to the internet. It also lets you place your backend systems, such as databases or application servers, in a private-facing subnet with no internet access. Amazon VPC lets you to use multiple layers of security, including security groups and network access control lists, to help control access to Amazon EC2 instances in each subnet.
Amazon Virtual Private Cloud aims to provide a service similar to private clouds using technology such as OpenStackor HPE Helion Eucalyptus. However, private clouds typically also use technology such as OpenShiftapplication hosting and various database systems. Cloud security experts warned there can be compliance risks, such as a loss of control or service cancellation in using public resourceswhich do not exist with in-house systems. If transaction records are requested from Amazon about a VPC using a National security letterthey may not even be legally allowed to inform the customer of the breach of the security of their system. This would be true even if the actual VPC resources were in another country.The API used by AWS is only partly compatible with that of HPE Helion Eucalyptus and is not compatible with other private cloud systems so migration from AWS may be difficult. This has led to warnings of the possibility of lock-in to a specific technology.
Amazon VPC provides advancedsecurity featuresthat allow you to perform inbound and outbound filtering at the instance and subnet level. Additionally, you can store data inAmazon S3and restrict access so that it’s only accessible from instances inside your VPC. Amazon VPC also hasmonitoring featuresthat let you perform functions like out-of-band monitoring and inline traffic inspection, which help you screen and secure traffic.
With Amazon VPC's simple set-up, you spend less time setting up, managing, and validating, so you can concentrate on building the applications that run in your VPCs. You can create a VPC easily using theAWS Management ConsoleorCommand Line Interface (CLI). Once you select from common network setups and find the best match for your needs, VPC automatically creates the subnets, IP ranges, route tables, and security groups you need. After configuring your network, you can easily validate it with Reachability Analyzer.
Amazon VPC helps you control your virtual networking environment by letting you choose your own IP Address range, create your own subnets, and configure route tables to any available gateways. You can customize the network configuration by creating a public-facing subnet for your web servers that has access to the internet. Place your backend systems, such as databases or application servers, in a private-facing subnet. With Amazon VPC, you can ensure that your virtual private cloud is configured to fit your specific business needs.
Setting up an AWS private cloud isn’t rocket science if you follow the proper steps. Here’s a clear pathway to help you operate the AWS Management Console and adjust the Amazon Virtual Private Cloud properly.
Step 1: Create Your VPC
Step 2: Set Up Subnets in AWS VPC
Step 3: Configure Routing and Security
Step 4: Deploy Your Resources
Both AWS and Amazon Virtual Private Cloud are constantly evolving. Here are some of the latest insights you should know:
VPC Lattice – Simplifies service-to-service networking across accounts and regions.
IPv6-Only Subnets – Supports modernised cloud networking with IPv6.
VPC Reachability Analyzer Enhancements – Provides deeper insights into network connectivity.
AWS Network Firewall Enhancements – Strengthen traffic filtering and security policies.
A well-designed VPC does more than just get things to work. It also plans growth and security. Keep the following AWS networking basics in mind:
Many organisations need to extend their on-premises infrastructure to AWS. Here’s how you can smoothly merge your data center with your VPC:
Option 1: AWS Site-to-Site VPN
Option 2: AWS Direct Connect
Option 3: AWS Transit Gateway
Host a simple, public-facing website
Host a basic web application, such as a blog or simple website, in a VPC and gain the additional layers of privacy and security afforded by Amazon VPC. You can help secure the website by creating security group rules which allow the web server to respond to inbound HTTP and SSL requests from the internet while simultaneously prohibiting the web server from initiating outbound connections to the internet. Create a VPC that supports this use case by selecting"VPC with a Single Public Subnet Only"from the Amazon VPC console wizard.
Host multi-tier web applications
Host multi-tier web applications and strictly enforce access and security restrictions between your web servers, application servers, and databases. Launch web servers in a publicly accessible subnet while running your application servers and databases in private subnets. This will ensure that application servers and databases cannot be directly accessed from the internet. You control access between the servers and subnets using inbound and outbound packet filtering provided by network access control lists and security groups. To create a VPC that supports this use case, you can select"VPC with Public and Private Subnets"in the Amazon VPC console wizard.
Back up and recover your data after a disaster
By using Amazon VPC for disaster recovery, you receive all the benefits of a disaster recovery site at a fraction of the cost. You can periodically back up critical data from your data center to a small number of Amazon EC2 instances with Amazon Elastic Block Store (EBS) volumes, or import your virtual machine images to Amazon EC2. To ensure business continuity, Amazon VPC allows you to quickly launch replacement compute capacity in AWS. When the disaster is over, you can send your mission critical data back to your data center and terminate the Amazon EC2 instances that you no longer need.
Extend your corporate network into the cloud
Move corporate applications to the cloud, launch additional web servers, or add more compute capacity to your network by connecting your VPC to your corporate network. Because your VPC can be hosted behind your corporate firewall, you can seamlessly move your IT resources into the cloud without changing how your users access these applications. Furthermore, you can host your VPC subnets inAWS Outposts, a service that brings native AWS services, infrastructure, and operating models to virtually any data center, co-location space, or on-premises facility. Select"VPC with a Private Subnet Only and Hardware VPN Access"from the Amazon VPC console wizard to create a VPC that supports this use case.
Securely connect cloud applications to your datacenter
An IPsec VPN connection between your Amazon VPC and your corporate network encrypts all communication between the application servers in the cloud and databases in your data center. Web servers and application servers in your VPC can leverage Amazon EC2 elasticity and Auto Scaling features to grow and shrink as needed. Create a VPC to support this use case by selecting"VPC with Public and Private Subnets and Hardware VPN Access"in the Amazon VPC console wizard.
Get started with Amazon VPC
You can automatically provision AWS resources in a ready-to-usedefault VPC. Configure this VPC by adding or removing subnets, attaching network gateways, changing the default route table, and modifying the network ACLs.
Create additional VPCs from the Amazon VPC page on the AWS Management Console by selecting the "Start VPC Wizard" button. You will be presented with four basic network topologies. Select the one that most closely resembles the network topology that you’d like to create and click the "Create VPC" button. You can then customize the topology further to fit your needs more closely. Shortly after, you can start launching Amazon EC2 instances inside your VPC.
AWS VPC's security is two-fold: firstly, AWS VPC uses security groups as a firewall to control traffic at the instance level, while it also uses networkaccess control listsas a firewall to control traffic at the subnet level. As another measure of privacy, AWS VPC provides users with ability to create "dedicated instances" on hardware, physically isolating the dedicated instances from non-dedicated instances and instances owned by other accounts.
AWS VPC is free, with users only paying for the consumption ofEC2 resources. However, if choosing to access VPC via a Virtual Private Network (VPN), there is a charge.
There are few more terms you need to understand while learning AWS VPC and launching EC2 instances.
Security groups:
A security group acts as a virtual firewall that controls the traffic for one or more instances. When you launch an instance, you associate one or more security groups with the instance. You add rules to each security group that allow traffic to or from its associated instances.
We can think of office access cards, as equivalent to “security groups”. Depending on how granular you want the security, you can apply security groups at different levels in AWS. Same applicable for office building too. You can put access cards at the building level (or) floor level (or) some other measures.
Public VPC with OPEN security groups:

This is the case where you launch instances into a VPC and the security groups associated with VPC/instance open up ALL ports; this is a VERY BAD practice. The equivalent in our office building analogy would be a building without any access cards. EVERYONE can come and go to any floor or suite.
Public VPC with Restricted security groups:
This is the case where you launch instances into a VPC and the security groups associated with a VPC/instance restricts open ports; this is a GOOD practice. The equivalent in our office building analogy would be a building with access cards. Only people who have access cards can enter into the building and get around inside.
Private VPC:

Private VPC is a VPC with ONLY private subnets. These resources within a private VPC aren’t accessible to the outside world without either special tools (or) VPC peering.
Though this is not a perfect analogy, we can think of “washrooms” in your office building as private VPC (in other words VPC with private subnets). People who don’t have access to building can’t access the washrooms.
In summary, the combination of VPC + Availability Zone + Subnet + private/public ip addresses +security groups are the AWS resources which form the required infrastructure to support EC2 instances running in a secured and scalable environment. Understanding working principles of these resources will help users in properly configuring and utilizing these resources.
In the event that the default VPC gets deleted, it is advised to reach out to AWS support for restoration. Therefore, you’ll only want to delete the default VPC only if you have a good reason.
A properly designed VPC is the backbone of a safe and flexible AWS system. Gaining clarity about the AWS networking basics is a must for managing cloud performance, whether you're a cloud architect, developer, or business leader.
Follow the best practices to protect your VPC and avoid cyber attacks.
Design with growth in mind–use multiple AZs and effective subnet strategy.
Connect with in-house networks for a smooth hybrid cloud experience.
Stay conscious of AWS innovations to keep your VPC at peak performance.
Want to future-proof your AWS career? Explore the AWS certification Benefits and get ahead in the cloud industry.
Confused about our certifications?
Let Our Advisor Guide You